What is Arthritis of the Thumb?
Arthritis is an inflammatory condition of the joints. There are several types of arthritis. The most common type is osteoarthritis, or wear-and-tear arthritis. Osteoarthritis can affect the joint at the base of the thumb. Thumb arthritis is more common in women than men, and usually occurs after the age of 40 years.
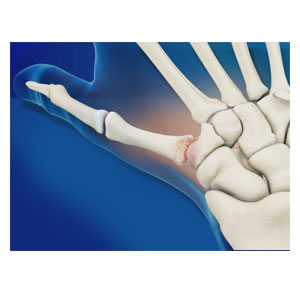
Symptoms of Arthritis of the Thumb
The symptoms of arthritis of the thumb usually include swelling, pain, stiffness and malformation, all of which interfere with the use of the hand.
Diagnosis of Arthritis of the Thumb
Your doctor can usually make the diagnosis of thumb arthritis by examining the thumb. X-rays of the joint may be ordered to determine the severity of the disease, and identify any bone spurs or calcium deposits.
Treatment for Arthritis of the Thumb
Non-surgical treatment methods for relieving pain in an arthritic joint include activity modification, antiinflammatory medications, and use of splints and steroid injections. Surgery is usually considered when non-surgical treatment fails to give relief. There are different surgical procedures that can be used:
- Arthroplasty: In this procedure, your surgeon removes the affected joint and sometimes replaces it with an artificial implant. Frequently, a tendon from the forearm is used to reconstruct the worn out joint. In certain situations, some new implants and devices can be used to reconstruct the joint.
- Arthrodesis: A fusion, also called an arthrodesis, involves the removal of the joints and fusing the bones of the joint together using metal wires or screws. Even though this surgery eliminates all motion at the base of the thumb, the resulting fusion is very durable.
This surgery is usually necessary when the joints are severely damaged or has limited mobility. An arthrodesis may also be necessary if there is damage to the surrounding ligaments and tendons, a failed previous arthroplasty, or when heavy manual use is expected.
Your surgeon will discuss options and help you decide which type of surgery is the most appropriate for you.
Rehabilitation Following Surgery for Arthritis
Following surgery, a rehabilitation program, often involving an occupational or physical hand therapist, may help to regain hand strength and movement. You may need to use a postoperative splint for a while after surgery to help protect the hand while it heals. Additionally, you may need to restrict activities for a minimum of 12 weeks to let the joint reconstruction heal properly. Although recovery is slow, you should be able to resume your normal activities within a few months of surgery.
