
Are you considering hip reconstructive surgery? This essential guide walks you through the process, helping you understand when it’s necessary, what it entails, and the recovery and care that follows. Discover how this surgery aims to relieve your hip pain and restore mobility, and learn about your next steps for a life with less pain.
Key Takeaways
- Hip reconstructive surgery, including replacement with a prosthetic hip implant, aims to relieve severe hip pain, restore mobility, and allow patients to engage in activities they enjoy.
- Hip reconstruction becomes necessary due to conditions like arthritis, hip dysplasia, or fractures that result in severe pain and mobility issues, and involves procedures such as hip replacement, resurfacing, and arthroscopy.
- Following hip reconstruction surgery, rehabilitation and recovery focus on managing pain, preventing blood clots, and progressively improving mobility, with a typical recovery period of two to eight weeks.
👉Also Read: The Art and Science of Hip Reconstructive Surgery at Academy Orthopedics
Exploring Hip Reconstructive Surgery
Hip reconstructive surgery is a life-changing procedure undertaken to repair or replace a damaged hip joint, often involving the replacement of damaged or diseased parts with an implant. The specialists in orthopaedics at Academy Orthopedics employ the latest surgical techniques to carry out these procedures.
The primary goals of this treatment include relieving severe hip pain, restoring mobility, and allowing patients to return to activities they enjoy once more.
Understanding Hip Reconstruction
Often, the necessity for hip reconstruction arises when the hip joint has suffered significant degeneration. This degeneration impairs movement and causes pain, severely affecting the patient’s quality of life. The most prevalent cause for such degeneration is damage of the cartilage due to arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
These forms of arthritis damage the joint, leading to debilitating pain and stiffness. When non-surgical treatments fail to alleviate these symptoms, hip reconstruction emerges as the best solution. The procedure replaces the damaged joint with a prosthesis, restoring functionality and drastically reducing pain.
The Role of Hip Prosthesis
A crucial component of hip reconstructive surgery is the hip implant (replacement), also known as the hip prosthesis. Designed to mimic the ball-and-socket action of the natural hip joint, a prosthesis comprises a metal, ceramic, or plastic ball and a corresponding socket lining. The materials used, often including metal, ceramic, and hard plastic, are chosen for their durability and ability to facilitate smooth movement.
The attachment of the prosthesis to the bone can be cemented for immediate fixation, or uncemented, which allows natural attachment through bone growth into the prosthetic’s pores but requires some limited activity during the integration period.
The Anatomy of the Hip Joint
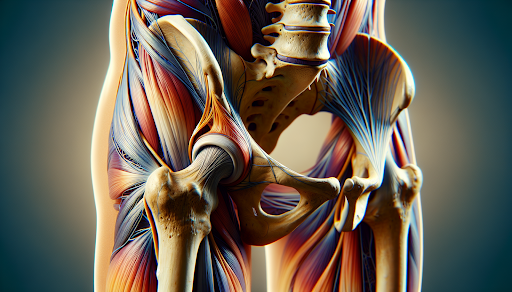
Understanding the procedure requires a basic understanding of the anatomy of the hip joint. The joint is a ball-and-socket joint. It consists of the head of the thighbone, also called the femur, and the pelvic bones. The pelvis, made up of three bones—the ilium, ischium, and pubis—forms the socket part of the joint, known as the acetabulum. The femur, or thighbone, has a spherical femoral head that creates the ball part of the joint.
The stability in the hip joint is provided by a fibrocartilaginous lining called the labrum, which attaches to the socket (acetabulum). Key supporting ligaments, including the iliofemoral, pubofemoral, ischiofemoral, and ligamentum teres, contribute to this stability as well. These structures work in harmony to facilitate movement and bear weight, making the hip joint a crucial part of our musculoskeletal system.
Indications for Hip Reconstruction
Hip reconstruction surgery is not the first line of treatment for hip issues. It becomes a consideration under specific circumstances, primarily when certain health conditions lead to severe pain and mobility issues. These conditions can include:
- Arthritis
- Hip dysplasia
- Femoroacetabular impingement
- Hip fractures
- Osteonecrosis
- Perthes disease
If you are experiencing the following symptoms, these could be indications for hip reconstruction:
- Persistent groin pain
- Difficulty with activities such as climbing stairs
- Discomfort that interferes with sleep
- Localized swelling or bruising in the hip area
When these symptoms persist and cause severe hip pain even after non-surgical treatments, specialists may recommend hip reconstruction surgery as the most suitable procedure based on your individual needs.
Preparing for Your Hip Surgery
If you are considering hip reconstructive surgery, preparation is key. The initial consultation for this procedure typically lasts 1 to 2 hours, during which:
- Your medical history is gathered
- A physical examination is conducted
- X-rays are taken
- The consultation process is completed
You should wear comfortable and loose clothing that can easily expose the hip area for examination during this consultation.
Additionally, you are advised to bring the following items for an effective consultation:
- Prior images like MRI scans and x-rays
- Related radiologist reports
- Operative Note and Implant Sticker sheet from any previous hip surgery
- Current treatment prescriptions
- All test results for an anesthetist consultation during the pre-operative period.
Consultation with an Orthopaedic Surgeon
A consultation with an orthopaedic surgeon is an essential step in your journey to hip reconstruction. The initial visit aims to:
- Reduce your pain
- Accurately diagnose the issue
- Identify the necessity of additional diagnostic tests
- Facilitate your return to desired activities
Part of the consultation includes a clinical evaluation to identify the cause of joint pain.
During this consultation, a personalized plan is created to achieve a comfortable level of health and promote healing for you. A thorough discussion of surgical procedures, potential risks, and expected outcomes is part of this consultation, and it is crucial to have this dialogue with a qualified orthopaedic surgeon.
👉Also Read: How to Find the Best Orthopedic Surgeon for Your Needs
What are the Procedures involved in Hip Reconstruction?
When it comes to hip reconstruction, several procedures are available. The choice of procedure depends on various factors, including the specific condition of your hip joint, your overall health, and the surgeon’s expertise.
The procedures performed in hip reconstruction include osteotomy, hip replacement, also called total hip arthroplasty, hip resurfacing, and hip arthroscopy.
Osteotomy
Osteotomy is a surgical procedure that involves cutting and reshaping a bone to improve its alignment and function. In the context of hip reconstruction, this technique is used to reshape the hip socket, ensuring a better fit with the head of the femur. By optimizing the alignment and movement of the hip joint, osteotomy can significantly enhance stability and function. This procedure not only aims to reduce pain and improve mobility in the hip joint but also helps to prevent future injuries in the area.
Hip Replacement
During hip replacement surgery, the surgeon removes the damaged parts of the hip joint and replaces them with an implant to improve mobility and reduce pain. A total hip replacement involves replacing all components of the joint, while a partial hip replacement only replaces the damaged bone. These hip replacement surgeries can help alleviate pain and improve mobility.
Hip Resurfacing
Hip resurfacing is a surgical procedure that serves as an alternative to total hip replacement surgery, particularly for younger and more active patients. Unlike traditional hip replacement, which involves removing and replacing the entire hip joint, hip resurfacing preserves both the ball and socket of the hip joint. During the procedure, the orthopedic surgeons trim and cap the femoral head with a smooth metal covering, while the hip socket is also fitted with a metal cup. This method maintains more of the patient’s natural bone structure and aims to provide a more natural-feeling joint post-surgery.
By using durable prosthetic materials to resurface the hip joint, hip resurfacing aims to reduce pain, improve hip function, and extend the joint’s lifespan. This approach allows for a greater range of motion and activity levels compared to traditional hip replacement, making it a suitable option for those seeking to maintain an active lifestyle.
Hip Arthroscopy/ Minimally Invasive Options
In recent years, minimally invasive hip reconstructive surgery techniques, such as hip arthroscopy, have gained popularity. These techniques use smaller incisions, reducing the amount of trauma to the soft tissues. Arthroscopic surgeries involve the use of a tube-like instrument called an arthroscope. Additionally, small surgical instruments are used during the procedure.
The Surgical Procedure: Step by Step
Now that we have explored the different hip reconstruction procedures, it’s time to walk you through the surgical process. Whether you are undergoing a hip replacement, hip resurfacing, or an osteotomy, the surgical procedure typically lasts around two hours and may involve either a spinal block or general anesthesia.
The main aim of the surgery is to relieve pain and alleviate stiffness in the hip joint.
In the Operating Room
Once you’re in the operating room, you’ll find yourself in a meticulously sterilized environment, featuring specialized lighting to ensure a clear view for the surgical team. Prior to surgery, the surgical team washes their hands rigorously and dons sterilized gowns, gloves, and protective gear to maintain a sterile environment.
Equipment such as anesthesia machines, monitors, and specialized arthroscopic equipment, along with essential surgical tools, are prepared and ready for the operation at the hospital or surgery center.
During the Operation
During the operation, the damaged ball of the femur and socket of the acetabulum are replaced with precisely selected artificial components to fit your individual needs. The surgical team may employ either the posterior or anterior approach for hip replacement based on which best suits your condition.
The size of the incision made during surgery is determined by several factors, including your body size, specific joint issues, and the surgeon’s preferred method.
After the Surgery
Once the operation is complete, the patient will be moved to a recovery room where the immediate care process begins. The immediate postoperative care includes:
- Blood clot prevention after hip reconstruction surgery
- Managing post-surgical pain with alternating heat and ice treatments
- Taking pain medication prior to physical therapy sessions
- Getting the patient up and walking with physical therapy
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Following your surgery, rehabilitation and recovery become the primary focus. At Academy Orthopedics, we offer a comprehensive rehabilitation program after hip reconstruction that is tailored to each patient’s individual needs to facilitate recovery and the transition from hospital to home. The recovery period from hip replacement surgery typically ranges from two to eight weeks, varying based on your health condition.
Rehabilitation may begin within the first 24 hours after surgery with the goal of walking using assistance and progressively improving mobility. Your rehabilitation may include various components like targeted therapy, medications, prescribed exercise routines, and nutritional advice.
Home and Outpatient Care
Upon your discharge from the hospital, adapting your home environment for safety and comfort during recovery from hip reconstruction is essential. You should consider installing adaptive equipment such as safety bars, raised toilet seats, and shower chairs. You’re also advised to organize your home space to create a safe recovery area where essential items are within reach.
Before leaving the hospital, you and your caregivers will be equipped with tips on caring for your new hip during the transition back home. This guidance will include how to manage daily activities using crutches, transitioning between furniture, and car travel to ensure safety. It’s also essential for you to have arrangements in place for help with household tasks and transportation following hip reconstructive surgery.
Long-Term Care and Maintenance of Your New Hip
Following your recovery, it’s important to focus on long-term care and maintenance of your new hip. Patients with hip replacements are encouraged to participate in low-impact activities as part of their long-term lifestyle, which can include walking, swimming, and biking. After an initial recovery period, you may also resume more demanding activities like bowling, dancing, horseback riding, golf, doubles tennis, and skiing if you were engaged in these pre-surgery and can perform them safely.
It’s essential to have regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon to keep track of the condition of your hip replacement. These appointments include X-rays and physical examinations and are scheduled for one year, two years, and subsequently every five years up to 15 years after the surgery.
The estimated lifespan of a hip joint replacement is between 15 to 30 years, with variations dependent on several factors such as your age, weight, and activity level.
Risks and Complications Associated with Hip Reconstruction
Despite the high success rate of hip reconstructive surgeries, it’s important to be aware of potential risks and complications. Symptoms of a potential infection following hip reconstruction surgery can include:
- Persistent fever
- Increasing redness or swelling of the wound
- Drainage
- Increased pain
- Infection
- Fracture
- Blood clots
These symptoms warrant immediate medical attention. Treatment of infections after hip reconstruction may involve antibiotics or surgery, such as debridement, and in severe cases may require removal and replacement of the implant.
In addition to infections, another potential risk is implant failure, particularly in young and active individuals. This could lead to the potential need for revision surgery. To prevent infections, the following measures are taken:
- Antibiotics are administered around the time of surgery
- The operating time is kept as brief as possible
- Measures are taken to minimize operating room traffic and reduce contamination risks.
👉Also Read: Beyond Surgery: Hip Joint Reconstruction – Your Comfort, Our Priority
Schedule an Appointment at Academy Orthopedics
If you’re dealing with hip pain or considering hip reconstructive surgery, don’t hesitate to seek help. Academy Orthopedics takes great pride in providing quality care for patients of all ages. Our board-certified physicians treat many different types of orthopedic problems, offering both non-surgical and surgical solutions.If you wish to be advised on the most appropriate treatment, please call (770) 271-9857 to schedule an appointment or click to request an appointment online.
