Hip arthroscopy vs hip arthroplasty: which procedure is right for you? Hip arthroscopy uses small incisions to repair or diagnose joint issues with a quicker recovery. Hip arthroplasty, or hip replacement, replaces the joint entirely to relieve severe pain and improve mobility. This article compares the pros, cons, and recovery times of both to help you decide.
Key Takeaways
- Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure used to diagnose and treat conditions like labral tears, femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), and synovitis with benefits including faster recovery times and reduced postoperative pain compared to traditional open surgery.
- Hip arthroplasty, or total hip replacement, involves replacing damaged hip joint components with prosthetics and is recommended for patients with severe arthritis or significant joint damage, providing substantial pain relief and improved mobility over a longer recovery period.
- The choice between hip arthroscopy and hip arthroplasty depends on factors such as the extent of joint damage, patient’s age, overall health, and lifestyle goals, and should be determined in consultation with an experienced orthopedic surgeon.
Discover expert hip care at Academy Orthopedics. Whether you’re exploring the possibilities of hip arthroscopy for precise diagnosis and treatment, or considering the transformative benefits of hip arthroplasty, our team is here to guide you. With a focus on advanced surgical techniques and compassionate patient care, Academy Orthopedics ensures every step of your journey is supported by our experienced physicians—Dr. Jesse Seidman, Dr. Jonathan Katz, and Dr. James Duckett. Schedule your consultation today and take the first step towards a healthier, more active you.
👉Also Read: The Art and Science of Hip Reconstructive Surgery at Academy Orthopedics
Understanding Hip Pain and Its Causes
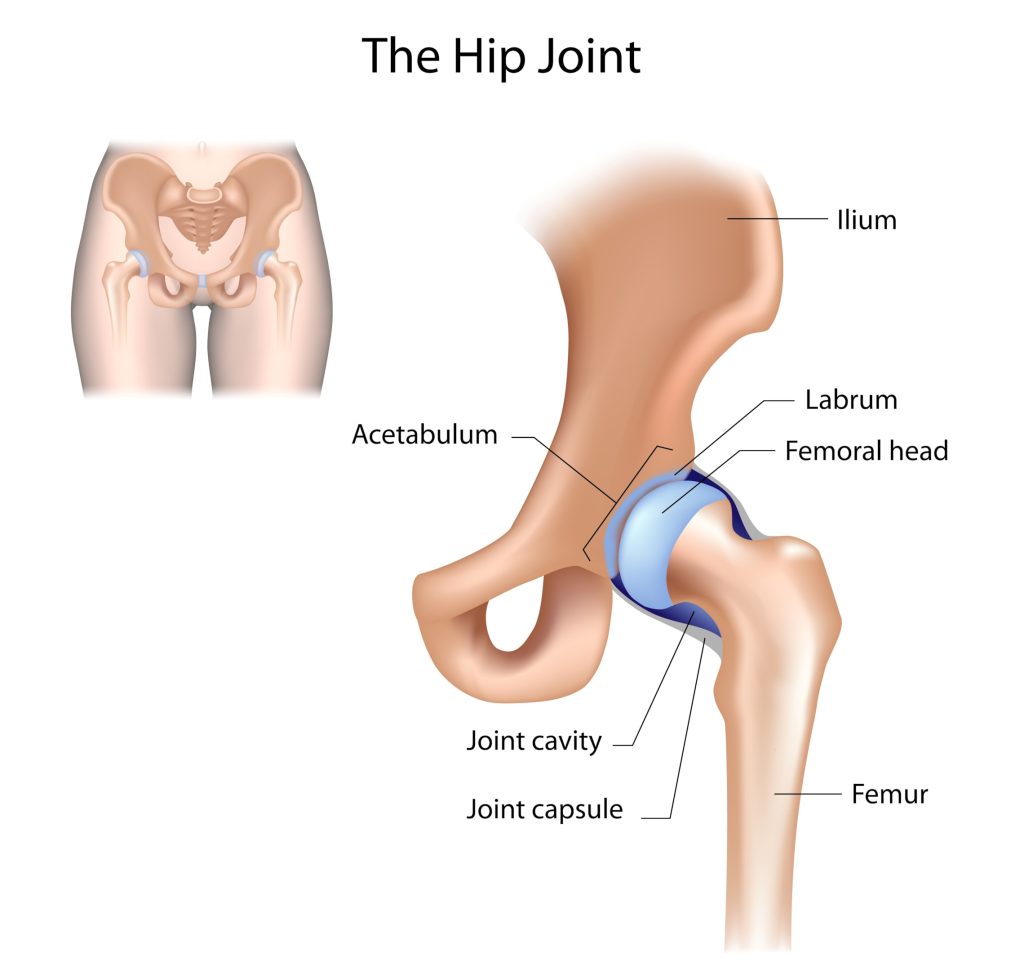
Hip pain, with its diverse origins, each carrying unique characteristics and treatment implications, is a multifaceted issue. The hip joint, ingeniously designed by nature, bears the brunt of repeated motion and substantial wear and tear. However, it’s not indestructible. A variety of factors such as hip arthritis, cartilage degradation, and muscle and tendon wear can contribute to hip pain.
In some cases, what feels like hip pain might actually be a reflection of an underlying issue in the back, rather than the hip itself.
Other potential culprits include:
- Hip fractures, which are particularly common in older patients with weaker bones
- Infections in the bones or joints
- Conditions like osteonecrosis, where the bone loses its blood supply
One of the main causes of hip pain is femoral acetabular impingement (FAI) and hip impingement syndrome, both of which can be classified as hip injuries. These conditions result from irregular contact between the hip joint’s ball and socket, typically caused by bone spurs or abnormal bone shapes. This can lead to pain, especially during movement and exercise, and may contribute to the development of arthritis over time. The location and nature of the pain can provide valuable clues for diagnosis. For instance, pain originating from the hip joint is often felt most acutely in the groin area.
Bursitis, the inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs cushioning the hip joint, can cause pain, especially during activities like standing up, walking, or climbing stairs. Some patients may even experience a condition known as snapping hip syndrome, characterized by a snapping sensation or sound in the hip, which can be accompanied by pain.
What is Hip Arthroscopy?
Hip arthroscopy is a groundbreaking method for diagnosing and addressing hip conditions. This minimally invasive procedure utilizes an arthroscope, a small camera attached to a fiber-optic light source, to visualize the inside of the hip joint. The arthroscope is inserted through tiny incisions, allowing the surgeon to:
- Examine the joint’s structures in real time on a video monitor
- Accurately diagnose the condition
- Perform necessary treatments simultaneously
- Minimize trauma to the surrounding tissues
This technique offers numerous benefits, including faster recovery times and reduced post-operative pain.
The procedure is an exceptional example of modern medical technology. Typically, the surgeon makes two or three small incisions, each about a quarter of an inch in length, around the hip joint. Through these tiny portals, specialized instruments are introduced alongside the arthroscope. This arrangement enables the surgeon to precisely navigate the hip’s intricate anatomy to address issues like torn cartilage, bone spurs, or inflamed synovium.
The beauty of hip arthroscopy lies in its versatility. It can be used to:
- Diagnose mysterious hip pain
- Remove loose bodies floating in the joint
- Repair torn labrums
- Reshape bone in cases of hip impingement
By offering a less invasive alternative to traditional open surgery, hip arthroscopy has opened up new possibilities for treating hip conditions that were once challenging to address through minimally invasive surgery.
Benefits of Hip Arthroscopy
Hip arthroscopy holds numerous and substantial advantages over traditional open hip surgery. Some of these advantages include:
- Smaller incisions, resulting in minimal trauma to the surrounding ligaments, muscles, and tissues
- Less pain, minimal scarring, and a lower risk of infection for the patient
- Less bleeding during surgery, which can contribute to a smoother recovery process
These benefits make hip arthroscopy a preferred option for many patients.
The possibility of a quicker recovery is one of the most attractive facets of hip arthroscopy. Patients often experience quicker healing times compared to traditional open surgery, with many able to return home the same day as the procedure. This rapid recovery trajectory extends to rehabilitation as well.
With less tissue damage to overcome, patients can often begin physical therapy sooner, leading to faster restoration of hip function and mobility. Additionally, the lower risk of complications associated with hip arthroscopy, including a reduced risk of infection, makes it an attractive option for many patients and surgeons alike.
This combination of benefits – less pain, faster recovery, and lower complication rates – has made hip arthroscopy an increasingly popular choice for treating a wide range of hip conditions.
Conditions Treated by Hip Arthroscopy
Hip arthroscopy, as an effective treatment for diverse hip conditions, widens the scope for patients seeking relief from hip pain and dysfunction. One of the most common issues addressed through this procedure is labral tears.
The labrum is a ring of cartilage that lines the acetabular socket, providing stability and cushioning to the hip joint. When this cartilage is torn, it can cause pain, catching sensations, and limited mobility. Hip arthroscopy allows surgeons to repair or trim the damaged labrum, restoring the joint’s smooth function.
Another significant condition that can be addressed through hip arthroscopy is femoroacetabular impingement (FAI). This condition occurs when there’s abnormal contact between the femoral head (ball) and the acetabulum (socket) of the hip joint, often due to excess bone growth.
Left untreated, FAI can lead to cartilage damage and early onset of arthritis. Through arthroscopic techniques, surgeons can reshape the bone, removing the excess growth and restoring proper joint mechanics. This not only relieves pain but can also potentially delay the progression of arthritis.
Additionally, hip arthroscopy can be used to remove loose bodies within the joint, address synovitis (inflammation of the joint lining), and treat certain types of hip instability. The versatility of this procedure makes it a valuable tool in the orthopedic surgeon’s arsenal for treating a wide range of hip conditions.
👉Also Read: How to Find the Best Orthopedic Surgeon for Your Needs
When is Hip Arthroscopy Recommended?
Recommending hip arthroscopy stems from a thorough assessment of the patient’s condition, symptoms, and reaction to conservative treatments. Typically, hip arthroscopy is considered when non-surgical approaches have failed to provide adequate relief. These conservative measures might include:
- Rest
- Physical therapy
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Corticosteroid injections
If a patient continues to experience persistent hip pain, stiffness, or limited range of motion despite these interventions, hip arthroscopy may be the next step in their treatment journey. Hip arthroscopy is particularly well-suited for younger, active patients who are experiencing hip pain but do not yet require a full hip replacement. This demographic often includes athletes or individuals with physically demanding jobs who have developed conditions like labral tears or FAI.
The minimally invasive nature of arthroscopy allows these patients to potentially return to their activities more quickly than they would after a more extensive surgery. However, it’s important to note that hip arthroscopy is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The procedure is most effective for specific conditions and may not be suitable for patients with advanced arthritis or certain types of hip deformities.
The decision to proceed with hip arthroscopy should always be made in consultation with an experienced orthopedic surgeon who can assess the individual’s unique situation and determine the most appropriate course of action.
What is Hip Arthroplasty?
Commonly referred to as hip replacement surgery, hip arthroplasty, is a significant breakthrough in treating severe hip conditions. This surgical procedure involves replacing parts of the hip joint with artificial components, with the primary goal of relieving pain and improving mobility.
Unlike hip arthroscopy, which aims to preserve and repair the existing joint structures, hip arthroplasty involves removing damaged bone and cartilage and replacing them with prosthetic components designed to mimic the natural function of the hip joint.
The procedure itself demonstrates the inventive spirit of contemporary orthopedic surgery. During a hip replacement, the surgeon performs the following steps:
- Makes an incision over the hip to expose the joint.
- Carefully dislocates the femur (thigh bone) from the acetabulum (hip socket).
- Meticulously removes and prepares the damaged surfaces of both the ball and socket.
- Places the artificial components, typically made of metal, ceramic, or high-grade plastic. The femoral component is fitted into the hollow center of the thigh bone, while the acetabular component is fixed into the pelvic bone.
- Carefully repairs the surrounding muscles and tissues before closing the incision.
This intricate process results in a new, artificial hip joint that can dramatically improve a patient’s quality of life by reducing pain and restoring function.
Types of Hip Arthroplasty
Hip arthroplasty is available in various forms, each customized to cater to specific patient needs and conditions. The most common type is total hip replacement, which involves replacing both the ball (femoral head) and socket (acetabulum) parts of the hip joint.
This comprehensive approach is typically recommended for patients with widespread joint damage, such as those suffering from severe osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. In a total hip replacement, the entire joint is reconstructed using artificial components, providing a complete solution for patients with extensive hip problems.
On the other hand, partial hip replacement, also known as hemiarthroplasty, involves:
- Replacing only the ball portion of the hip joint
- Often recommended for older patients who have experienced certain types of hip fractures, particularly those affecting the femoral neck
- In these cases, replacing just the femoral head can provide sufficient pain relief and functional improvement without the need for more extensive surgery.
The choice between total and partial hip replacement depends on various factors, including:
- The patient’s age
- Overall health
- The extent of joint damage
- The specific nature of their hip condition
Your orthopedic surgeon will carefully evaluate these factors to determine which type of hip arthroplasty is most appropriate for your case.
Benefits and Risks of Hip Arthroplasty
Hip arthroplasty provides a spectrum of substantial benefits for patients afflicted with severe hip conditions. The primary advantage is the potential for substantial pain relief. Many patients who have lived with chronic hip pain for years find that hip replacement surgery provides them with a level of comfort they haven’t experienced in a long time.
Along with pain reduction comes improved joint function. Patients often report a dramatic increase in their ability to perform daily activities, from walking and climbing stairs to engaging in light recreational activities. This restoration of mobility can have a profound impact on a person’s quality of life, independence, and overall well-being.
However, like any major surgery, hip arthroplasty carries potential risks and complications of which patients should be cognizant. Some of the most common risks include:
- Blood clots, which can be dangerous if they travel to the lungs
- Infection, although modern surgical techniques and prophylactic antibiotics have significantly reduced this risk
- Fracture during or after the surgery, particularly in patients with weakened bones
- Dislocation of the new joint, especially in the early weeks after surgery, which is why patients are given specific precautions to follow
- Nerve damage
- Leg length discrepancy
- Loosening of the prosthetic components over time
While these risks are generally low, especially when the surgery is performed by an experienced orthopedic surgeon, patients must understand and discuss these potential complications with their healthcare provider before deciding to proceed with hip replacement surgery.
👉Also Read: Beyond Surgery: Hip Joint Reconstruction – Your Comfort, Our Priority
Indications for Hip Arthroplasty
Hip arthroplasty is typically suggested when conservative treatments fall short of providing sufficient relief from hip pain and dysfunction. One of the primary indications for hip replacement surgery is moderate to severe arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis.
These conditions cause progressive deterioration of the hip joint, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility that significantly impacts a patient’s quality of life. When the pain becomes severe enough to interfere with daily activities and sleep, and when non-surgical treatments no longer provide sufficient relief, hip arthroplasty may be the next step.
Hip replacement surgery is also indicated for certain hip fractures, particularly in older patients. These fractures can severely compromise the blood supply to the femoral head, leading to a condition called avascular necrosis or osteonecrosis.
In such cases, replacing the damaged joint components can restore function and alleviate pain more effectively than attempting to repair the fracture. Additionally, conditions like hip dysplasia, where the hip socket is abnormally shaped, may eventually require hip replacement if they lead to severe joint damage over time.
It’s important to note that the decision to proceed with hip arthroplasty is not based solely on the severity of joint damage visible on imaging studies. The patient’s symptoms and how they impact daily life play a crucial role. For instance, pain that persists even during rest and affects sleep quality is a strong indicator that more aggressive treatment may be necessary.
Difficulty in performing basic activities like walking, climbing stairs, or even putting on shoes can significantly diminish a person’s quality of life and may warrant consideration of hip replacement.
Comparing Hip Arthroscopy and Hip Arthroplasty
In resolving hip issues, both hip arthroscopy and hip arthroplasty provide viable solutions, but their approach and application differ considerably. Hip arthroscopy is characterized by its minimally invasive nature. It involves smaller incisions and is generally less stressful on the body compared to hip arthroplasty. This translates to less postoperative pain, reduced scarring, and typically a faster initial recovery period.
Hip arthroscopy is particularly well-suited for addressing specific internal joint problems like labral tears, removal of loose bodies, or reshaping bone in cases of femoroacetabular impingement.
On the other hand, hip arthroplasty, or total hip replacement, is a more extensive procedure recommended for people with significant damage to their cartilage or severe arthritis. While it involves a larger incision and more extensive tissue dissection, it offers a comprehensive solution for patients with widespread joint damage.
Hip replacement can provide dramatic pain relief and functional improvement for those who have exhausted other treatment options. The recovery time for hip arthroplasty is generally longer than that of hip arthroscopy, but it often results in more substantial long-term improvements for patients with advanced hip conditions.
Recovery Time and Postoperative Care
The recovery process and postoperative care markedly differ between hip arthroscopy and hip arthroplasty, mirroring the varying extent of these procedures. For hip arthroscopy, the recovery time is generally shorter, with full recovery typically achieved within about six weeks. However, patients may need up to 12 weeks before they can return to sports or heavy exercise. This relatively quick recovery is one of the key advantages of the arthroscopic approach, allowing patients to resume their normal activities sooner.
Postoperative care following hip arthroscopy includes:
- Taking prescribed pain medications
- Using crutches to limit weight-bearing on the operated hip
- Engaging in regular physical therapy exercises to restore normal hip function
- Following a healthy diet and avoiding smoking to promote faster healing
- Restricting heavy lifting and strenuous exercises for the first few weeks after surgery
Physical therapy plays a vital role in the recovery process, helping patients with an injured hip regain strength and range of motion in the patient’s hip joint.
In contrast, recovery from hip arthroplasty generally takes longer due to the more extensive nature of the surgery. Postoperative care following total hip replacement involves specific precautions to protect the new joint and ensure proper healing. These precautions often include:
- Avoiding certain movements that could dislocate the new hip, such as bending the hip past a right angle or crossing the legs.
- Using an elevated toilet seat and a grabber tool to avoid bending too far.
- Early mobilization is encouraged to reduce the risk of blood clots, but this is done under the careful guidance of healthcare professionals.
While the initial recovery period may be longer for hip replacement, many patients find that their pain levels and overall function continue to improve over several months following the surgery.
Choosing the Right Procedure
Choosing between hip arthroscopy and hip arthroplasty involves a complex process that necessitates the careful consideration of various factors. The most critical step in this decision-making process is a consultation with an experienced orthopedic surgeon. These specialists have the expertise to evaluate your specific condition, taking into account factors such as:
- The extent of joint damage
- Your age
- Overall health
- Lifestyle
- Personal goals
They can provide a comprehensive assessment of your hip condition and guide you toward the most appropriate treatment option.
👉Also Read: Beyond Surgery: Nurturing Your Hip Health with Our Holistic Patient-Centered Care
Take Control of Your Hip Health—Schedule Your Consultation Today
In the matter of hip care, the expertise and experience of your healthcare provider can play a pivotal role. At Academy Orthopedics, we bring a wealth of experience and a commitment to patient care that dates back to our founding in 1985. Our team of board-certified orthopedic surgeons are leaders in the field of orthopedic surgery. We specialize in diagnosing and treating hip pain, offering a range of advanced hip reconstruction options designed to restore mobility and enhance your quality of life.
Our accredited on-site surgery center provides both surgical and non-surgical solutions, ensuring that we can offer the most appropriate treatment for your specific needs. Whether you’re dealing with chronic hip pain, considering hip arthroscopy, or exploring the possibility of hip replacement, our expert team is here to guide you through every step of your journey to improved hip health.
Don’t let hip pain hold you back any longer – take the first step towards a pain-free life by scheduling a consultation with our team at Academy Orthopedics today.
