
Are you struggling with shoulder pain or limited mobility caused by a rotator cuff tear and wondering if Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy could help? PRP therapy is a regenerative treatment that harnesses your body’s own healing potential to repair damaged tissue and promote recovery. For many patients, it offers a promising, minimally invasive alternative to surgery—or can be used alongside traditional treatments to enhance healing.
At Academy Orthopedics in Buford, GA, our orthopedic surgeons are dedicated to providing advanced, evidence-based treatments that help patients restore strength, function, and confidence in their shoulders. PRP therapy has become an increasingly effective option for addressing rotator cuff injuries and supporting long-term joint health.
In this article, our Buford orthopedic specialists discuss how PRP therapy works for rotator cuff tears, its potential benefits, and what factors to consider before deciding if this treatment is right for you.
Understanding Rotator Cuff Tears
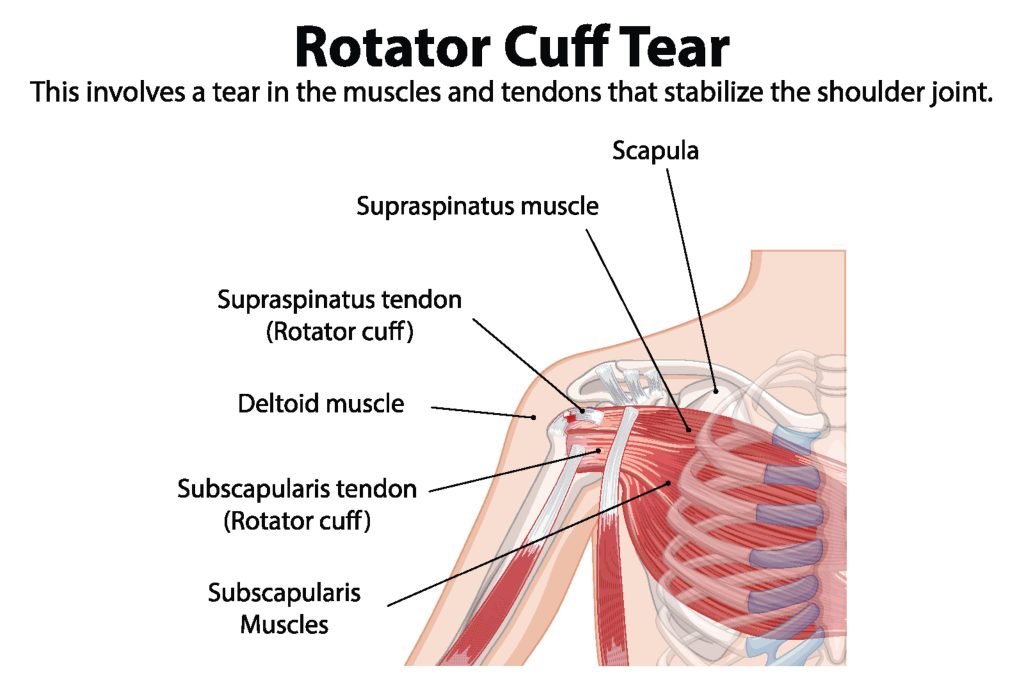
Each year, approximately 200,000 Americans undergo surgery to repair a torn rotator cuff, with an additional 400,000 having procedures for related tendonitis or partial tears. Most of these injuries result from age-related wear and tear, but individuals who heavily rely on their shoulders—such as athletes involved in throwing sports or those performing strenuous manual labor—are at higher risk. Research suggests that the prevalence of rotator cuff tears may exceed 50 percent in people over the age of 80, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
The rotator cuff is an essential structure of the shoulder joint, composed of four muscles and their associated tendons that surround the upper arm bone (humerus). These muscles include:
- Supraspinatus Tendon
- Infraspinatus Tendon
- Teres Minor
- Subscapularis Tendon
Together, these muscles work in coordination to stabilize the shoulder joint and enable a wide range of arm movements. The primary function of the rotator cuff is to keep the humeral head securely positioned within the shallow shoulder socket, ensuring smooth and controlled motion.
Rotator cuff tears can occur for several reasons:
- Acute injuries — such as a fall on an outstretched arm or lifting something heavy — can cause a sudden tear.
- Degenerative changes — many tears develop gradually over time due to repetitive overhead movements or natural wear and tear associated with aging.
- Athletic activities — athletes who frequently use overhead motions, like baseball pitchers, swimmers, or tennis players, face a higher risk of tendon injury.
A torn rotator cuff can significantly affect shoulder function, often leading to pain, weakness, and restricted range of motion. Depending on the extent of the damage, tears are classified as partial-thickness, where only part of the tendon is frayed or torn, or full-thickness, where the tendon is completely detached. Understanding the type and severity of your rotator cuff injury is key to selecting the most effective treatment approach.
In some cases, rotator cuff tendinopathy—a condition where the tendons become inflamed and weakened—can precede or accompany a tear. Chronic partial supraspinatus tears, one of the most common forms of tendinopathy, may cause ongoing shoulder pain and functional limitations.
Recognizing the early signs of a rotator cuff injury is critical. Prompt evaluation and treatment can prevent further damage and allow you to explore advanced healing options such as Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy, which supports tissue regeneration and helps restore shoulder strength and mobility.
Symptoms of Rotator Cuff Injuries
Recognizing the symptoms of a rotator cuff injury is the first step toward seeking timely and effective treatment. One of the most common signs is persistent shoulder pain, which can range from a dull, constant ache to sharp, intense discomfort. This pain often worsens at night, making it difficult to sleep on the affected side.
In addition to general pain, many individuals experience sharp discomfort during specific movements, such as lifting the arm overhead, reaching behind the back, or performing everyday tasks like combing hair or dressing. Shoulder weakness is also common, limiting your ability to lift or lower the arm with ease.
Other symptoms may include popping or crackling sounds when moving the shoulder and chronic discomfort that persists over time. These symptoms can significantly impact daily life and reduce overall shoulder function.
If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to consult an orthopedic specialist. A thorough evaluation can confirm the diagnosis and help determine the most appropriate treatment plan, which may include Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy, physical therapy, or other interventions designed to restore shoulder strength and mobility.
What is Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy?
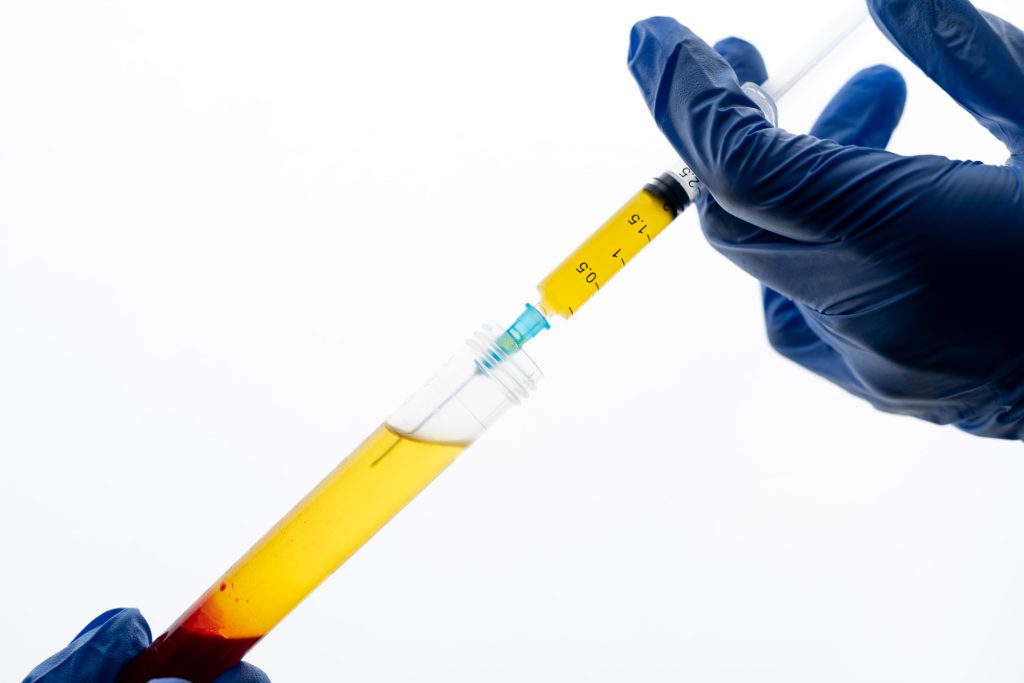
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy is a regenerative treatment that harnesses the body’s own healing potential to promote tissue repair and recovery. PRP is derived from a small sample of the patient’s blood, which is then processed to concentrate the platelets. These platelets are rich in growth factors and bioactive molecules that play a critical role in the body’s natural healing processes.
This innovative treatment has become increasingly popular in sports medicine and regenerative orthopedics, providing new options for patients with chronic tendon injuries, rotator cuff tears, and other musculoskeletal conditions.
How PRP Promotes Healing
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy supports tendon healing and tissue regeneration by harnessing the body’s natural repair mechanisms. Its effects can be grouped into several key areas:
Cellular Growth and Collagen Production
Activated platelets release growth factors and bioactive molecules—such as insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β)—that stimulate tenocyte proliferation (tendon cells) and collagen synthesis. Collagen is a primary structural protein in tendons, and its production is critical for restoring tendon strength, flexibility, and integrity after injury. PRP also enhances fibroblast activity, supporting the production of type I collagen, which is essential for healthy tendon structure.
Inflammation Reduction
PRP helps modulate the inflammatory response at the injury site by influencing cytokine activity. This anti-inflammatory effect creates a more favorable environment for tissue repair and can provide pain relief, particularly for patients dealing with chronic tendon injuries. By reducing excessive inflammation, PRP allows the body’s natural healing processes to proceed more efficiently.
Tissue Remodeling and Regeneration
Direct application of PRP to injured rotator cuff tendons maximizes the local concentration of growth factors, promoting tissue remodeling and regeneration. PRP stimulates cellular signaling pathways that enhance vascularization, improving blood flow and nutrient delivery to the affected tissue. This supports long-term tendon health and functional recovery.
Support for Comprehensive Recovery
PRP is most effective when combined with a tailored rehabilitation program, including physical therapy, strengthening exercises, and activity modification. By working synergistically with these interventions, PRP not only accelerates healing but can also help restore full shoulder function and reduce the risk of re-injury.
Through these multifaceted mechanisms, PRP therapy has become a valuable tool in regenerative orthopedics, offering patients a minimally invasive option to support tendon repair, reduce pain, and improve overall shoulder strength and mobility.
Mechanisms of PRP in Tendon Repair
PRP supports tendon repair through multiple mechanisms, primarily by stimulating growth factors and modulating inflammation. The concentrated growth factors in PRP promote the healing and regeneration of damaged tendons by:
- Enhancing tenocyte proliferation – Tenocytes, the cells responsible for maintaining tendon tissue, are stimulated to multiply, aiding in tendon repair.
- Increasing collagen synthesis – Collagen provides structural support to tendons, and PRP encourages the production of new collagen fibers, strengthening damaged tissue.
In addition to promoting cellular growth, PRP plays a key role in regulating inflammation, which is critical for effective tendon healing. Its anti-inflammatory effects help by:
- Increasing levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF).
- Reducing chronic inflammation, which can impede tissue repair in longstanding tendon injuries.
- Supporting vascular regeneration through the stimulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), improving blood supply to the injured tendon.
By combining growth factor stimulation with inflammation modulation, PRP creates an optimal environment for tendon repair and tissue regeneration. Leveraging the body’s natural healing mechanisms, PRP therapy offers a promising, minimally invasive approach to treating rotator cuff injuries and other tendon-related conditions.
Current Research on PRP for Rotator Cuff Injuries
Recent studies suggest PRP therapy may benefit patients with chronic partial rotator cuff injuries, though the evidence remains mixed. Some clinical trials demonstrate that PRP injections lead to better functional outcomes than physical therapy alone, while both approaches show progress over time.
Studies using dual PRP injections have shown sustained benefits at 2-year follow-up for partial tears, demonstrating safety and consistent results in patients who have failed conservative treatment.
While promising, long-term studies remain necessary to fully assess PRP’s sustained benefits. Standardization of PRP preparation techniques, including platelet concentration and leukocyte presence, is crucial for maximizing efficacy and ensuring consistent clinical outcomes. The effectiveness does vary significantly between patients, emphasizing the need for individualized treatment approaches.
PRP therapy represents a growing, less invasive option for rotator cuff injuries, particularly for patients seeking alternatives to rotator cuff surgery. As research evolves, we continue to refine our understanding of optimal candidates, preparation protocols, and combination therapies that maximize patient outcomes.
Partial vs. Full-Thickness Tears and PRP Effectiveness
Rotator cuff tears are classified as partial-thickness or full-thickness, each with unique characteristics and treatment considerations.
- Partial-thickness tears affect only a portion of the tendon and are common among athletes and individuals performing repetitive overhead movements. These tears can lead to pain, weakness, and reduced performance, but the tendon remains partially intact.
- Full-thickness tears involve complete separation of the tendon from the bone, often resulting in significant pain, loss of strength, and functional limitations.
PRP therapy has shown promising results for partial-thickness tears:
- It can reduce pain in both the short and long term.
- The growth factors in PRP stimulate tendon repair and collagen production.
- It may accelerate healing, supporting improved shoulder function and mobility.
For full-thickness tears, PRP is generally not considered a standalone solution. These injuries often require surgical repair to restore proper tendon function. While PRP may provide supportive benefits alongside surgery or rehabilitation, it cannot fully replace invasive treatment for severe tears.
Consultation Process with an Orthopedic Surgeon
When dealing with a rotator cuff tear, consulting an experienced orthopedic surgeon is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan. Choosing a shoulder specialist can significantly increase the likelihood of a successful recovery, as these surgeons are trained in the latest techniques and advancements for treating rotator cuff injuries.
The consultation typically begins with a thorough review of your medical history and a physical examination of the shoulder. Your orthopaedic surgeon may also recommend imaging tests, such as MRI or ultrasound, to assess the severity of the tear and discuss potential treatment approaches. Personal recommendations from family, friends, or colleagues can also provide valuable insights into a surgeon’s expertise and patient care style.
During your consultation, it’s important to discuss:
- Your symptoms and how they affect daily activities
- Your activity level and lifestyle demands
- Your treatment goals, including expectations for recovery and long-term function
This information helps your orthopedic surgeon develop a personalized treatment plan. Depending on your condition, this plan may include PRP therapy, physical therapy, or surgical intervention, ensuring that your treatment is tailored to your unique needs and promotes the best possible recovery.
PRP Injection Procedure
The PRP injection procedure is a minimally invasive treatment designed to deliver concentrated platelets directly to the injured tissue. The process involves several key steps:
- Blood collection – A small sample of the patient’s blood is drawn, usually from the arm.
- Centrifugation – The blood sample is placed in a centrifuge, which spins at high speeds to separate its components based on density.
- PRP preparation – The resulting concentrated solution of platelets suspended in plasma is known as platelet-rich plasma.
- Platelet activation – Before injection, the platelets may be activated using agents like calcium chloride or thrombin. Activation enhances the release of growth factors and bioactive molecules, maximizing the tissue-healing potential of the PRP.
- Injection – Next, the PRP is precisely injected into the injury site. Ultrasound can be used to help with placement, improving the effectiveness of the treatment.
Patients may require multiple PRP injection sessions, depending on the severity of the injury and the treatment protocol recommended by the orthopedic specialist. Sometimes a series of three injections is used to target the area of pain and inflammation. When performed properly, this step-by-step procedure aims to accelerate tissue healing, reduce inflammation, and support improved functional recovery.
Post-Procedure Care and Recovery Timeline
Proper post-procedure care is essential to maximize the effectiveness of PRP therapy and promote a smooth recovery. After treatment, patients are typically advised to rest the treated shoulder and avoid strenuous activities for a prescribed period. The use of a sling may be recommended to help immobilize the arm, protect the shoulder, and support the healing process during the early stages of recovery.
In the days following the PRP injection, patients may experience mild and temporary side effects such as localized pain, swelling, or bruising at the injection site. Applying ice packs several times a day can help minimize swelling and alleviate discomfort. Pain management strategies are usually coordinated by the physician and medical staff to ensure comfort and safety throughout recovery.
Rehabilitation plays a pivotal role in restoring shoulder strength, flexibility, and range of motion. A structured rehabilitation plan, developed collaboratively by the orthopedic specialist and physical therapist, is crucial for optimal outcomes. While full recovery from a rotator cuff injury may take approximately four to six months, adherence to post-injection rehabilitation guidelines can significantly enhance recovery speed and overall shoulder function.
Comparing PRP with Alternative Treatments
When evaluating treatment options for rotator cuff tears, it is important to compare Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy with conventional approaches such as physical therapy and surgical repair.
Physical therapy is often the initial treatment for rotator cuff injuries, emphasizing muscle strengthening, flexibility, and improved range of motion. It can be highly effective for mild to moderate tears; however, patients with more extensive or chronic damage may experience limited relief from rehabilitation alone.
Surgical treatment, including rotator cuff repair or shoulder joint replacement, is generally reserved for full-thickness tears or cases that do not respond to conservative therapies. While surgery can restore shoulder stability and function, it is invasive, carries higher procedural risks, and typically requires a longer recovery period compared to PRP therapy.
The long-term effectiveness of PRP relative to traditional surgical interventions continues to be studied, and further research is needed to establish standardized treatment protocols and confirm its sustained benefits. Moreover, insurance coverage for PRP therapy remains limited, which can affect patient accessibility.
Despite these limitations, PRP therapy offers a minimally invasive alternative that may delay or even prevent the need for surgery in patients with partial rotator cuff tears. By promoting pain reduction, tissue regeneration, and functional improvement, PRP can serve as an important intermediary treatment option.
Factors Influencing PRP Candidacy
Not every patient with a rotator cuff tear is an ideal candidate for Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy. Several factors influence whether PRP will provide meaningful results, and a thorough evaluation by an orthopedic specialist is essential before beginning treatment.
Severity and Type of Tear
PRP therapy tends to be more effective for partial-thickness tears or chronic tendon injuries where some of the tendon fibers remain intact. In contrast, full-thickness tears, where the tendon is completely detached from the bone, generally require surgical intervention rather than regenerative treatments like PRP.
Overall Health and Lifestyle
A patient’s general health can significantly impact the body’s healing capacity. Individuals who maintain a healthy lifestyle—through balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and adequate rest—often experience better outcomes. Conversely, underlying conditions such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, or chronic inflammatory diseases can slow the healing process and diminish the effectiveness of PRP.
Age and Cellular Regenerative Potential
While PRP uses the patient’s own blood, the concentration and quality of platelets naturally decrease with age. Younger patients or those with robust platelet activity may respond more favorably compared to older individuals with reduced regenerative potential. However, older adults can still benefit when PRP is combined with other conservative treatments, such as physical therapy.
Extent of Shoulder Degeneration
Patients with advanced degenerative changes in the rotator cuff or surrounding shoulder structures may not achieve the same results as those with acute or less severe injuries. PRP works best in tissues that retain some structural integrity and vascularity, allowing the growth factors to stimulate repair effectively.
Medications and Lifestyle Habits
Certain medications—particularly anti-inflammatory drugs or corticosteroids—can interfere with platelet activation and healing responses. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also hinder tissue regeneration and should be minimized before and after PRP treatment.
Adherence to Post-Treatment Protocols
Patient commitment to rehabilitation and activity modification plays a major role in recovery. Following post-injection instructions, participating in guided physical therapy, and avoiding activities that strain the shoulder are critical for achieving optimal results.
Importance of Choosing an Experienced Orthopedic Surgeon in Buford, GA
Selecting an experienced orthopedic surgeon is one of the most critical factors influencing the success of rotator cuff treatment and overall recovery. Whether considering Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy, conservative management, or surgical repair, the expertise and judgment of your orthopedic specialist play a vital role in determining the most effective treatment plan.
Accurate Diagnosis and Tailored Treatment Plans
An experienced orthopedic surgeon possesses the clinical knowledge and diagnostic skill to identify the precise nature and severity of the rotator cuff injury. Through a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and advanced imaging techniques such as MRI or ultrasound, they can accurately determine whether the condition involves inflammation, partial tearing, or a full-thickness rupture. This precision allows them to develop personalized treatment strategies that align with the patient’s age, activity level, and recovery goals.
Proficiency in Advanced and Minimally Invasive Techniques
Orthopedic surgeons with specialized training in shoulder and sports medicine are proficient in both non-surgical and surgical interventions, including arthroscopic techniques and regenerative procedures such as PRP injections. Their familiarity with the latest medical technologies and evidence-based practices ensures that patients receive the most effective and least invasive care possible, minimizing downtime and complications.
Enhanced Safety and Optimal Outcomes
Experienced surgeons are better equipped to manage complex cases, anticipate potential challenges, and adapt treatment approaches accordingly. Their expertise not only improves procedural accuracy—particularly in ultrasound-guided PRP injections—but also reduces the risk of infection, nerve injury, and post-procedural stiffness. This level of skill contributes to faster healing, reduced pain, and superior functional outcomes for patients.
Comprehensive Post-Treatment Support
A seasoned orthopedic surgeon provides more than just the initial treatment; they guide patients throughout the entire recovery journey. From coordinating physical therapy to monitoring progress and adjusting rehabilitation protocols, their ongoing involvement helps ensure steady improvement and long-term shoulder health.
Patient Confidence and Continuity of Care
Choosing a surgeon with a proven track record instills confidence and trust—key elements in a successful recovery. An experienced orthopedic specialist takes the time to educate patients, set realistic expectations, and maintain open communication throughout the treatment process, fostering a collaborative approach to care.
Selecting a Local Orthopedic Specialist
When selecting a local orthopedic specialist, there are several factors to consider to ensure you receive the best possible care. Checking a surgeon’s professional credentials, such as board certification and fellowship training, is essential for assessing their expertise in orthopaedic surgery. These credentials indicate that the surgeon has undergone rigorous training and adheres to high standards of practice.
Reviewing online ratings and feedback about a surgeon can help gauge the quality of care they provide, but it’s important to use reputable sources. Personal recommendations from family, friends, or colleagues can also provide valuable insights into a surgeon’s approach and patient care.
Consider the accessibility of the surgeon’s office, including location, parking, and how easy it is to schedule appointments. Ensuring that the surgeon’s office is conveniently located and accessible can make the treatment process more manageable and less stressful.
By taking these factors into account, you can select a local orthopedic specialist who meets your needs and provides high-quality care for your rotator cuff injury.
Take the Next Step Toward Shoulder Healing with Academy Orthopedics
If shoulder pain or limited mobility from a rotator cuff tear is affecting your daily life, it’s time to explore your treatment options with a trusted orthopedic team. At Academy Orthopedics in Buford, GA, our board-certified surgeons offer comprehensive care for a wide range of shoulder conditions, including rotator cuff tears, proximal biceps tendinitis, shoulder instability, frozen shoulder, and complex joint replacements.
Whether you are considering Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy as a minimally invasive option or require surgical intervention such as rotator cuff repair, shoulder arthroscopy, or shoulder replacement, our specialists create personalized treatment plans tailored to your unique needs. By combining advanced techniques with dedicated post-procedure support, we help patients regain strength, mobility, and confidence in their shoulders.
With convenient locations in Buford, Cumming, and Duluth, GA, Academy Orthopedics is ready to guide you through every step of recovery. Don’t let shoulder pain hold you back—schedule a consultation today by calling (770) 271-9857 or visiting our website. Take control of your shoulder health and get back to the activities you love with expert care you can trust.
Frequently Asked Questions
When is it necessary to consult a doctor for a rotator cuff tear?
You should consult a doctor if you are experiencing ongoing shoulder pain, weakness, or reduced mobility that does not improve with rest or simple home remedies. Key signs to watch for include:
- Difficulty lifting or moving your arm
- Pain that intensifies at night or disrupts sleep
- Popping, clicking, or grinding sensations in the shoulder
- Sudden loss of strength or range of motion following an injury
- Persistent shoulder discomfort lasting several weeks
Seeking timely evaluation from an orthopedic specialist ensures an accurate diagnosis and allows for the most effective treatment, whether through physical therapy, PRP injections, or surgical repair. Early intervention can prevent the tear from worsening and support a faster, more complete recovery.
Is it possible to heal or improve a rotator cuff tear without orthopaedic surgery?
Yes, in many cases, a rotator cuff tear can be managed and strengthened without surgical intervention, especially if the tear is partial or not severe. Non-surgical treatments typically include physical therapy to improve shoulder strength and flexibility, activity modification to reduce strain, anti-inflammatory medications, and targeted exercises to support tendon healing.
Regenerative treatments like Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy may also help promote tissue repair and reduce pain. While non-surgical approaches can be effective for mild to moderate tears, full-thickness tears or cases with significant weakness often require surgical repair to restore proper shoulder function. Consulting an orthopedic specialist can help determine the best individualized plan for recovery.
What activity restrictions should I follow after Platelet Rich Plasma injections?
After receiving a PRP injection for a rotator cuff injury, it is important to follow certain activity restrictions to ensure proper healing and maximize the treatment’s effectiveness. Patients are generally advised to rest the treated shoulder for at least 24 to 48 hours, avoiding strenuous movements or heavy lifting.
Use of a sling may be recommended initially to immobilize and protect the shoulder. Mild daily activities that do not strain the shoulder are usually allowed, but exercises or activities that involve overhead motions or repetitive use should be postponed.
Physical therapy and guided rehabilitation typically begin a few days to weeks after the injection, depending on your orthopedic specialist’s recommendations. Following these post-treatment guidelines helps reduce inflammation, promote tissue repair, and support a safe and effective recovery.
